티스토리 뷰
코드카타
할인 행사
문제

정현이는 마트의 회원이 되면 그 시점부터 10일 동안 할인을 받을 수 있다.
이 기간 동안 정현이가 원하는 제품과 수량을 모두 맞춰서
구매할 수 있는 날짜의 총 일수를 반환해야 한다.
입출력 예시
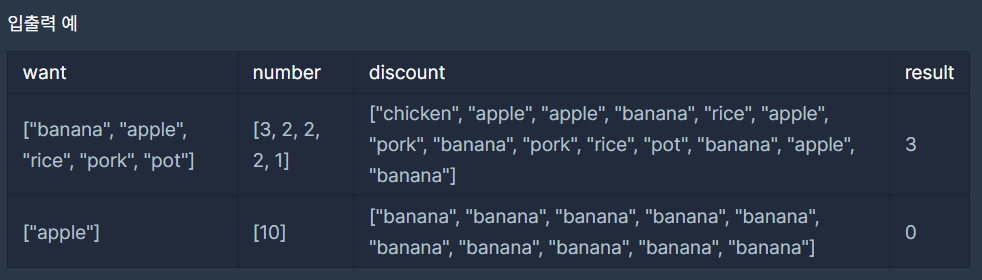
원하는 제품이 할인하는 날이 없을 땐 0을 반환한다.
zip()
fun main() {
val want = arrayOf("banana", "apple", "rice", "pork", "pot")
val number = intArrayOf(3, 2, 2, 2, 1)
val wantMap = want.zip(number.toTypedArray())
println(wantMap) // [(banana, 3), (apple, 2), (rice, 2), (pork, 2), (pot, 1)]
print(wantMap.toMap()) // {banana=3, apple=2, rice=2, pork=2, pot=1}
}zip함수는 두 개의 컬렉션을 짝지어 페어로 묶어준다.
zip함수를 호출하려면 두 컬렉션의 타입이 같아야 하기에
기본 배열에 해당하는 want를 제네릭 배열로 변환해줘야 한다.
Pair 객체들의 리스트는 맵으로 변환이 가능하다.
풀이
class Solution {
fun solution(want: Array<String>, number: IntArray, discount: Array<String>): Int {
// 정현이가 원하는 제품의 품목과 수량을 매핑한다.
val wantMap = want.zip(number.toTypedArray()).toMap()
var cnt = 0
// 할인 기간이 10일 미만의 경우는 검사하지 않음
for(i in 0..discount.size - 10){
// 현재 날짜(i)를 기점으로 10일간 할인하는 품목들
val currentDiscount = discount.slice(i until i + 10)
val currentCount = mutableMapOf<String, Int>()
// 현재 할인 품목 내 각 제품의 구매 횟수 세기
for (i in currentDiscount) {
currentCount[i] = currentCount.getOrDefault(i, 0) + 1
}
// 구매한 제품의 수량이 원하는 제품의 수량과 일치하는지 검사
var isSame = true
for ((i, c) in wantMap) {
if (currentCount.getOrDefault(i, 0) != c) {
isSame = false
break
}
}
// 조건을 만족하면 카운트 증가
if(isSame) cnt++
}
return cnt
}
}정현이가 원하는 제품과 수량을 매핑한 wantMap을 선언한다.
회원등록이 가능한 모든 날짜를 검사하여,
각 날짜별로 정현이가 구매할 수 있는 제품과 수량을 currentMap에 매핑한다.
이후 currentMap을 wantMap과 비교하여 각 맵의 요소가
일치하지 않는 경우가 없다면 카운트를 증가시킨다.
회고
예전에는 고봉밥 문제설명을 참 싫어했는데,
요새는 테스트 케이스를 친절하게 설명해준 문제가 호감이 간다.
골아픈 수학개념 공부를 요구하는 문제보다는
문해력을 요구하는 문제가 상대적으로 더 쉽게 느껴지는 탓일까?
이번 문제에서는 두 컬렉션을 연결하여 매핑하는 법과
두 맵이 일치하는지 검사하는 로직 짜는 법을 배울 수 있었다.
안드로이드 앱 개발 입문 3주차 정리 (2)
Layout
레이아웃이란?
레이아웃은 위젯을 배치하고, 크기와 위치를 지정하는 데 사용되는 컨테이너이다.
Linear Layout

자식 뷰들을 수평 혹은 수직으로 일렬 배치하는 레이아웃이다.
자식들은 중첩되지 않고,지정한 방향으로 쌓이는 형태이다.

자식들의 가중치(weight)를 설정해 너비를 지정할 수 있다.
Relative Layout

위젯을 서로 상대적으로 배치할 수 있는 레이아웃이다.
레이아웃 자체를 상대적 위치의 기준점으로 활용할 수도 있다.
자식 위젯들의 상대적 배치 관계를 지정해 주지 않는다면 위젯이 겹치게 된다.
TableLayout

위젯을 표 형식으로 배치할 수 있는 레이아웃이다.
테이블 레이아웃은 행의 개수만큼 TableRow를 포함하고,
TableRow는 각 행에 포함된 셀(View)를 포함한다.
Frame Layout
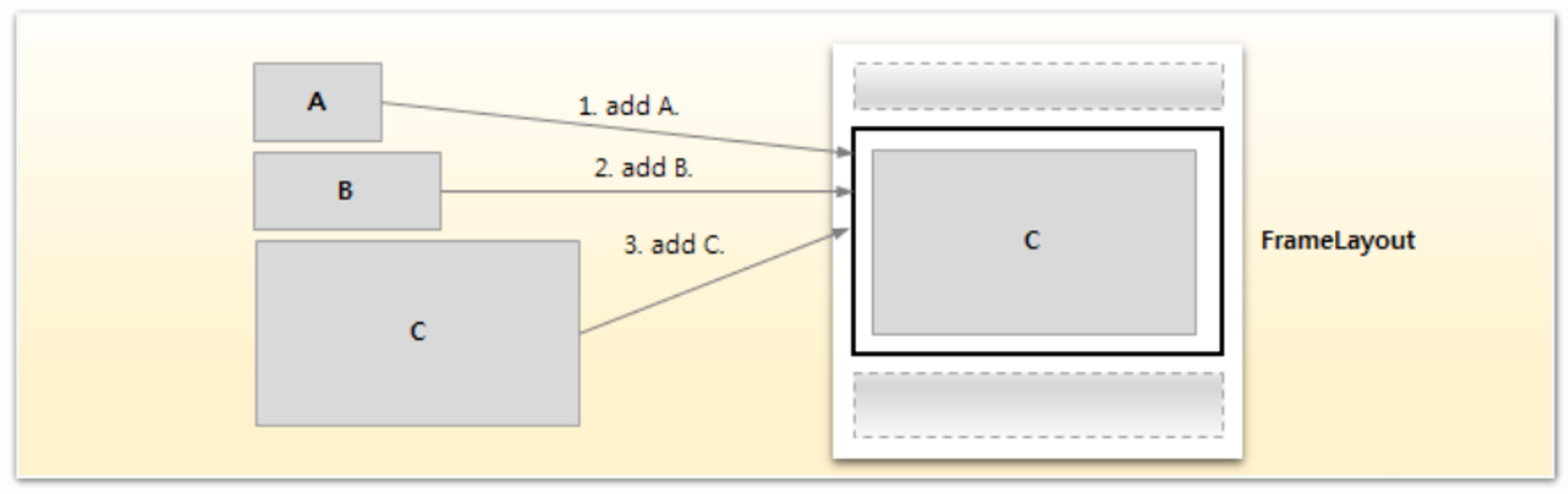
위젯 겹쳐서 배치할 수 있는 레이아웃이다.
가장 최근에 추가된 뷰가 가장 상위에 표시된다.
Constraint Layout
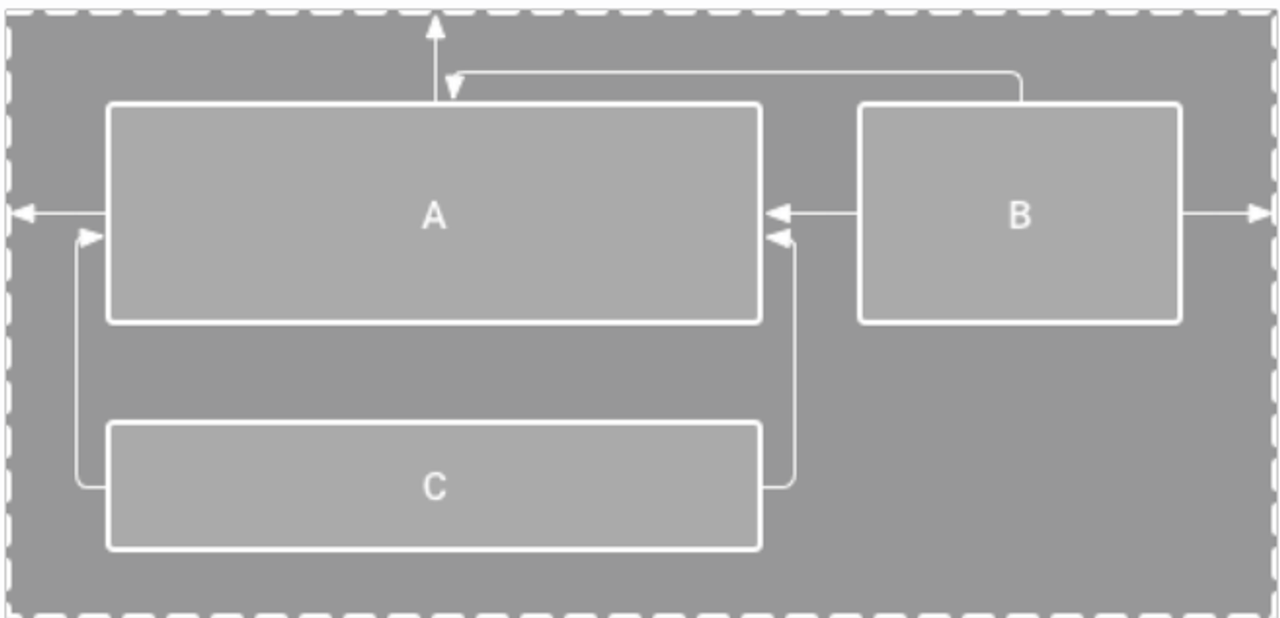
뷰의 위치와 크기를 제약 조건을 통해 유연하게 설정할 수 있는 레이아웃이다.
다양한 화면 크기와 대응하기 쉽고, 복잡한 UI를 효율적으로 설계할 수 있다.
레아이웃 속성
여백 속성
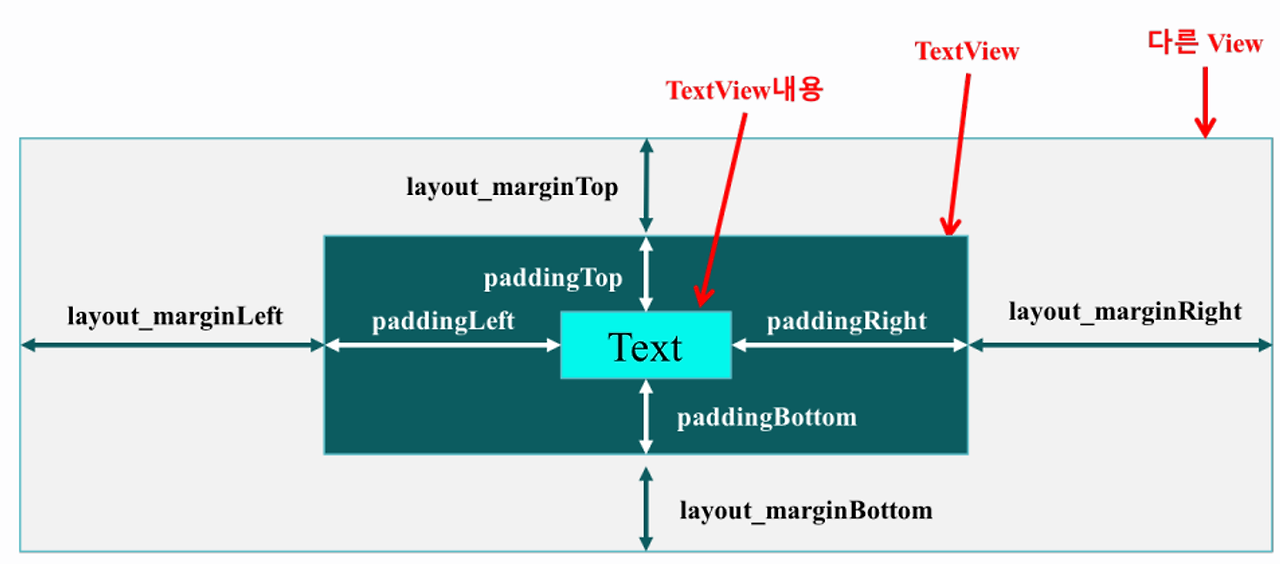
margin은 뷰의 외부 공간으로, 뷰와 다른 뷰 사이의 간격에 해당하고,
padding은 뷰의 내부 공간으로 뷰 경계와 뷰 콘텐츠 간의 간격에 해당한다.
정렬 속성
gravity는 뷰 내에 위치한 위젯들의 정렬 방식을 지정한다.
layout_gravity는 부모 레이아웃 내에서 뷰를 어떤 위치에 배치할지 지정한다.
뷰 내부의 콘텐츠 위치를 지정하고 싶을 땐 gravity를,
레이아웃 내의 뷰 위치를 지정하고 싶을 땐 layout_gravity를 써야한다.
레이아웃 실습
과제
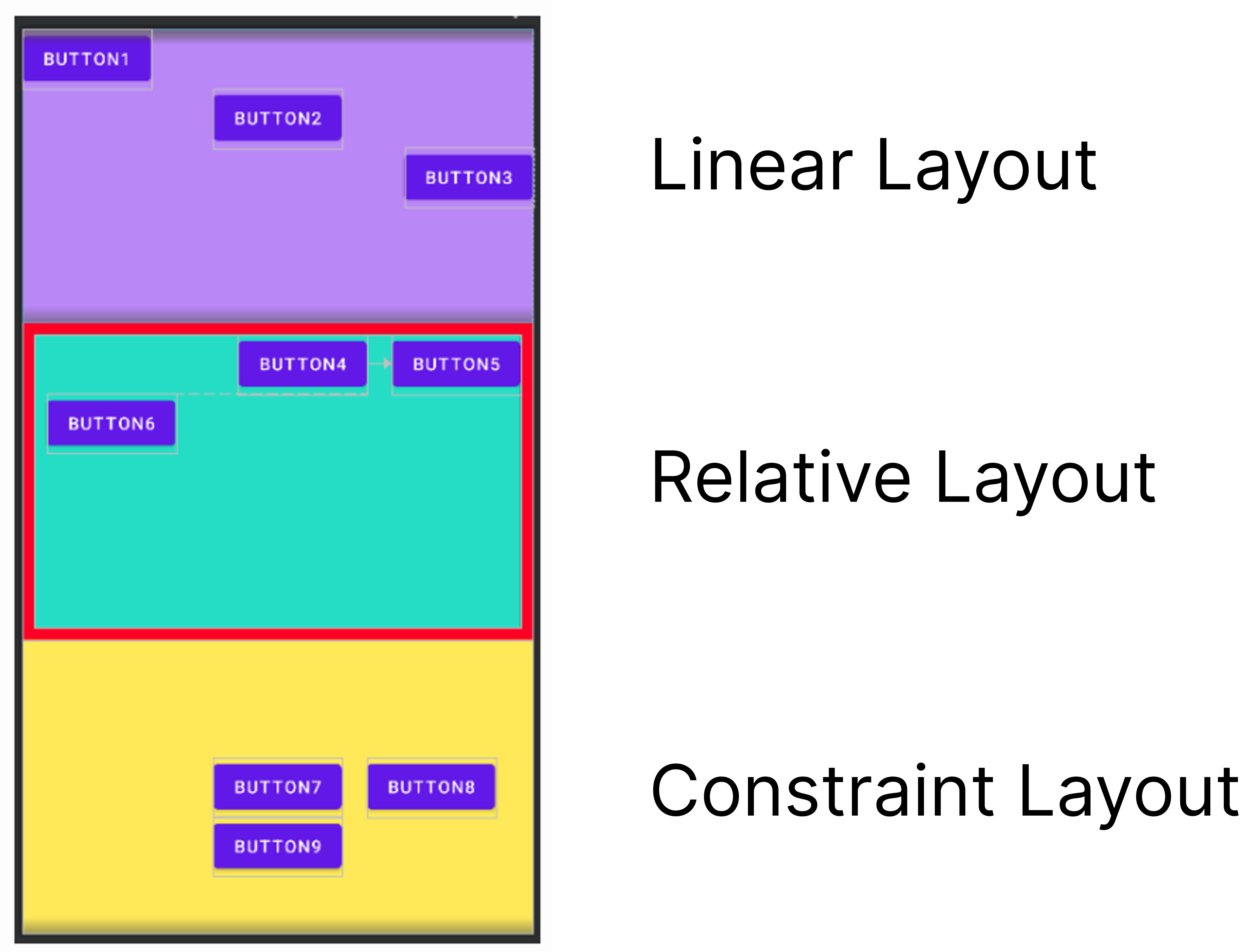
각 레이아웃을 활용하여 해당 화면을 구현하는 것이 실습과제이다.
레이아웃 배치
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
// ContraintLayout 속성 생략
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linearLayout1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:background="#BA87F7"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@id/linearLayout2"
app:layout_constraintVertical_weight="1">
</LinearLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/linearLayout2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:background="#25DDC5"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/linearLayout1"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@id/linearLayout3"
app:layout_constraintVertical_weight="1">
</RelativeLayout>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:id="@+id/linearLayout3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:background="#FDE958"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/linearLayout2"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_weight="1">
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>ContratinLayout안에 세 레이아웃을 배치하는 xml 코드이다.
세 레이아웃의 높이는 전부 같으며 화면이 꽉차도록 배치되어있다.
각 레이아웃의 높이를 0dp로 주고 세로 가중치를 전부 같은 값으로 준다.
그 다음 레이아웃의 위 아래 관계성을 명확히 지정해주면 된다.
위에서 아래로 레이아웃을 이어붙여준다.
맨 처음 레이아웃은 Top Contraint값을 parent로
맨 마지막 레이아웃은 Bottom Constraint값을 parent로 주면 된다.
LinearLayout
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />button 3개를 세로로 배치하고 layout_gravity 속성을 이용해 위치를 조정한다.
RelativeLayout
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginRight="20dp"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/button5"
android:text="Button4" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:text="Button5" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/button4"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:text="Button6" />Button5를 우측 상단에 고정한 후, Button4를 Button5 왼쪽에 배치하고 우측 마진값을 20dp 준다.
Button6을 Button4 아래로 배치하고 좌측 마진값을 10dp 준다.
Constraint Layout
<Button
android:id="@+id/button7"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button7"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button8"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="20dp"
android:text="Button8"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@+id/button7"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/button7"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/button7" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button9"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="Button9"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/button7" />Button7을 레이아웃 중앙에 배치하고 해당 버튼을 기준으로 다른 버튼을 배치한다.
Button8을 Button7 오른쪽 배치하고 세로 중앙정렬 후 좌측 마진값을 20dp 준다.
Button9를 Button7 아래로 배치하고 상단 마진값을 10dp 준다.
결과
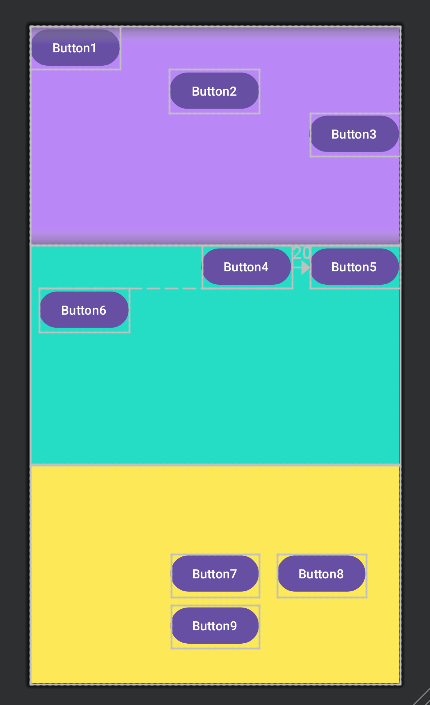
버튼 모양은 스타일 관련 건드리면 바꿀 수 있는데 귀찮아서 그냥 안했다.
각 레이아웃 위젯에 대한 이해도가 조금 늘게 되었다.
'내일배움캠프 > Android 국비지원' 카테고리의 다른 글
| TIL 28일차 (기능개발 - Kotlin) (0) | 2024.06.23 |
|---|---|
| TIL 27일차 (의상 - Kotlin) (1) | 2024.06.22 |
| TIL 25일차 (행렬의 곱셈 - Kotlin | 안드로이드 위젯 개념 정리) (1) | 2024.06.20 |
| TIL 24일차 (n^2 배열 자르기 - Kotlin | 앱개발 입문 2주차 정리) (0) | 2024.06.19 |
| TIL 23일차 (H-Index - Kotlin | 앱개발 입문 1주차 정리, 잘못된 풀이 분석하기) (0) | 2024.06.18 |
